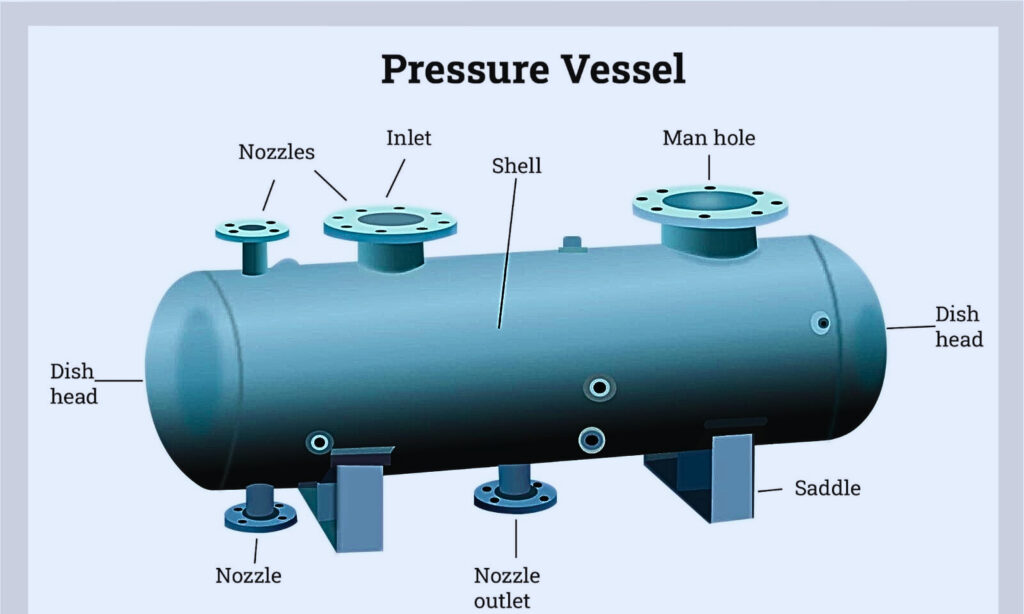
Understanding Pressure Vessels in Oil and Gas Refineries
In the intricate world of oil and gas refineries, pressure vessels play a pivotal role in various processes, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the refinery. Let’s explore some of the common types of pressure vessels used in this industry and their specific functions.
1. Separators
Separators are essential for dividing mixtures into their component phases, such as gas, oil, and water.
a. Three-phase separators: These vessels are designed to separate gas, oil, and water simultaneously.
b. Two-phase separators: These focus on separating gas from liquids, typically oil or water.
2. Drums
Drums are utilized to collect liquids or gases during the refining process.
a. Knockout drums: These are used to separate liquid droplets from gases, preventing them from entering downstream equipment.
b. Surge drums: These vessels handle fluctuations in flow rates, ensuring a steady process flow.
3. Reactors
Reactors facilitate critical chemical reactions under high pressure and temperature.
a. Hydrocracking reactors: These break down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more valuable ones.
b. Catalytic reforming reactors: These improve the quality of gasoline by restructuring hydrocarbon molecules.
4. Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers are crucial for transferring heat between two fluids, optimizing energy use within the refinery.
Shell and tube heat exchangers: These are commonly used due to their efficiency and effectiveness in various applications.
5. Columns
Columns are vital in distillation and absorption processes.
a. Distillation columns: These separate components of a mixture based on their boiling points.
b. Absorber columns: These absorb gases into a liquid, aiding in the removal of impurities.
6. Deaerators
Deaerators remove dissolved gases, typically from water, to prevent corrosion in the refinery’s equipment.
7. Filters
Filters are used to remove particulates from fluids, ensuring the purity and quality of the final product.
Coalescers: These filters combine small droplets into larger ones, making it easier to separate them from the fluid.
8. Autoclaves
Autoclaves are employed for high-temperature and high-pressure chemical reactions or material processing, ensuring thorough and efficient treatment.
9. Spheres and Bullets
These vessels store liquefied gases under high pressure.
a. Spherical vessels: These are commonly used for storing large volumes of gases like LPG.
b. Bullet tanks: These elongated cylindrical vessels are used for storing various gases under pressure.
10. Scrubbers
Scrubbers are designed to remove contaminants from gases.
Amine scrubbers: These are specifically used to remove acidic components such as CO2 and H2S from gas streams.
Each of these pressure vessels is meticulously designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of oil and gas refineries. Their roles are crucial in maintaining the integrity and productivity of the refining processes, ultimately contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the refinery.