Shells, integral components in numerous industrial structures such as pressure vessels and storage tanks, often necessitate meticulous fabrication techniques when constructed from multiple plates. In this article, we delve into the crucial considerations and processes involved in manufacturing shells using multiple plates, ensuring structural integrity and reliability.
Key Considerations:
1. Plate Joining:
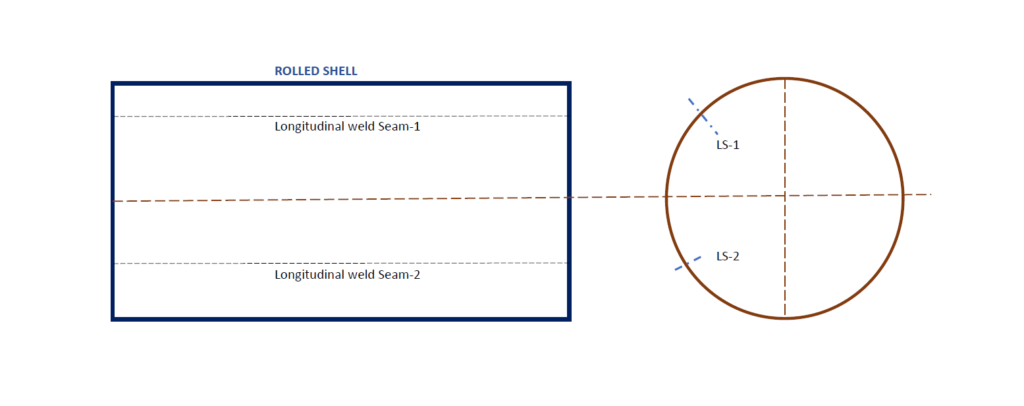
When the plate length falls short of accommodating the shell circumference, multiple plates are seamlessly joined together. This practice ensures the requisite dimensions while optimizing material usage and minimizing waste. Precise alignment and welding techniques are paramount to maintain structural integrity and prevent vulnerabilities at the seam.
2. Squareness Verification:
The squareness of joined plates must be rigorously assessed to ascertain dimensional accuracy and geometric alignment. Any deviations from squareness can compromise the integrity of the shell and hinder subsequent fabrication processes. Corrections, if needed, are promptly addressed to uphold quality standards and adherence to specifications.
3. Weld Reinforcement Preparation:
Before bending or rolling the joined plates to form the shell, weld reinforcement—excess weld metal—must be ground to ensure uniformity and facilitate smooth forming processes. Proper preparation of weld joints minimizes stress concentrations and enhances the overall weld quality, contributing to the structural robustness of the shell.
4. Radiographic Inspection:
Following bending or rolling of the joined plates, radiographic inspection becomes imperative, especially for critical applications where weld quality is paramount. Radiography aids in detecting internal defects, discontinuities, or imperfections that may compromise the integrity of the shell. This non-destructive testing method ensures compliance with stringent quality standards and regulatory requirements, providing assurance of structural reliability.
Fabrication Process:
- Plate Selection: Choose plates of suitable dimensions and material composition, considering factors such as shell diameter, operating conditions, and material properties.
- Plate Joining: Seamlessly join multiple plates using welding techniques, ensuring precise alignment and weld quality to maintain structural integrity.
- Squareness Verification: Assess the squareness of joined plates to verify dimensional accuracy and geometric alignment, making necessary corrections as per specifications.
- Weld Reinforcement Preparation: Grind excess weld metal to prepare weld joints for bending or rolling, ensuring uniformity and minimizing stress concentrations.
- Forming: Utilize bending or rolling techniques to shape the joined plates into the desired cylindrical form, maintaining dimensional accuracy and alignment throughout the process.
- Radiographic Inspection: Conduct radiographic testing post-forming to detect internal defects or discontinuities, ensuring compliance with quality standards and regulatory requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Implement stringent quality checks and inspections at each stage of the fabrication process to identify and rectify any deviations or defects, ensuring the production of high-quality shells.
- Finishing: Apply surface treatments or coatings as required to enhance corrosion resistance and prolong the service life of the shell, ensuring durability and reliability in diverse operating environments.